One of the success criteria in putting a centralized architecture in place is standardisation and simplification of real-time data interchange between applications
How an application bus works?
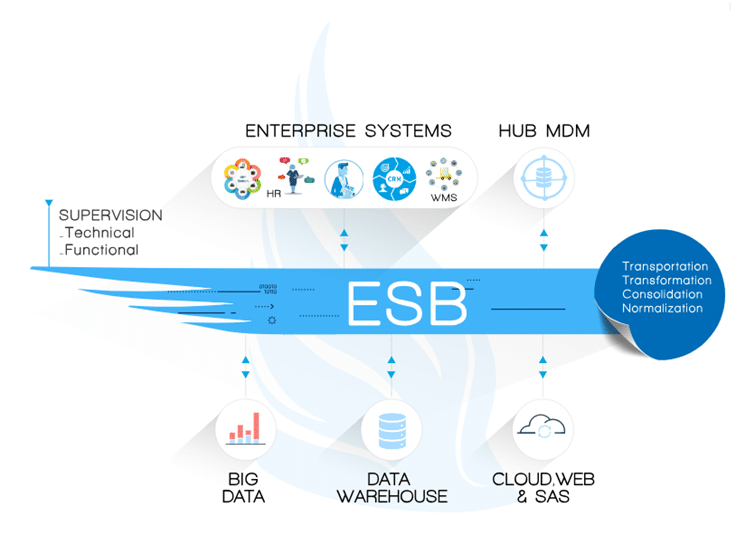
The application bus is the central component of Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) software. An Enterprise Service Bus can be defined as a set of tools that guarantee secure exchanges between the sources and targets of an information system. A middleware IT tool, the application bus can be represented as a channel for circulating information between applications, the purpose of which is to guarantee data routing and persistence.
The terms “application bus” and “ESB” are sometimes used interchangeably, as these two approaches are designed to ensure integration and communication between the applications and software of the Information System. They are at the heart of Service Oriented Architectures (SOA) and provide a response to the challenges posed by point-to-point integration (securing and managing exchanges, simplified IS evolution and maintenance, etc.). However, in our vision at Blueway, the application bus is one of the building blocks that make up the Enterprise Service Bus. The ‘Bus’, in fact!

How process (BPM) and data (ESB) integration can create value for IT and business departments ?
The way the Enterprise Service Bus works is very simple: the data exchange structure is standardised and, rather than making direct interfaces between software, the software will subscribe to the messages available on the bus that interest them. The application bus handles data transport, with the capacity to deliver very large volumes of data in real time.
The application bus acts as a universal translator, smoothing and organising the dialogue between the disparate software in the IS!
The 2 main advantages of the application bus
Unlike traditional interfaces, which are executed using procedure calls, setting up an enterprise application bus offers a number of advantages, but above all makes it possible to do two fundamental things:
1st fundamental action: complete and enrich the data
This operating mode also allows for greater scalability, as each application can update separately, and the Blueway application bus is also capable of supplementing messages by managing intermediate distribution circuits in order to enrich the data repository according to feedback from applications.
2nd fundamental action: Integrate data in asynchronous mode
The Enterprise Service Bus retrieves data messages and knows that it must deliver them to applications in the information system that have “subscribed” to these messages. But if an application is not immediately available, the application bus may not block the routing and integration of the data in the other available applications; it activates the “persistence” mode to continue delivering the message until the application in question becomes available again.

ESB vs ETL ? The distinction between is no longer relevant relative to today’s business requirements.
What is the added value of the Phoenix Blueway platform for managing your Application Bus and your Enterprise Service Bus?
All Blueway platform functions such as EAI (Enterprise Application Integration), ETL, Mashup and BPM (Business Process Management) connect to our application bus natively and graphically, without the need for development.
Other native tools and connectors provide dynamic information routing, integration, transformation and queue management mechanisms, authentication, encryption, etc. within this bus.
The magic of Phoenix lies in its ability to make the challenge of integrating applications simple!
Edouard Cante, Deputy Managing Director of Products at Blueway
Blueway simplifies the use of the application bus
The integrated Phoenix platform makes the use of the application bus for your inter-application data exchanges totally transparent: no lines of code to write, automated queuing and port management.
As with the entire Phoenix Blueway platform, you can do away with technical complexity!
The Blueway application bus can be integrated with other Enterprise Service Buses
The Data Foundation module of our Phoenix data platform is capable of integrating with other ESBs and middleware solutions. For example, if a new application natively integrates an Enterprise Service Bus that manages message transmission or consumption, the ESB already implemented with Blueway on existing applications can be retained and Blueway will connect the 2 Enterprise Service Buses so that you don’t have to re-configure anything.

Want to discuss interoperability challenges with an expert?





