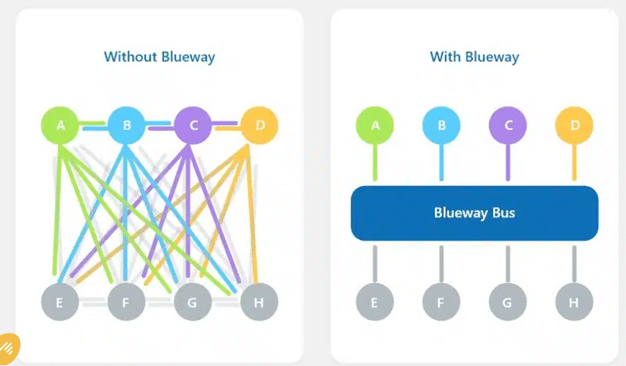
When attempting to represent data interchange between applications within an information system architecture (EAI for Enterprise Application Integration), any diagram, even for a well-ordered and structured organisation, will ultimately tend to resemble a plate of spaghetti! Over the years, point-to-point interfaces have been built, connecting individual applications in the IS for data interchange purposes, both internally and with partners external to the business.
This entails many pitfalls, and it is essential to identify the risks and limitations of using Excel as the core element of such processes :
- No control over or ability to anticipate any side effects caused by changing a given interface
- A vicious circle is formed, whereby rather than running the risk of changing an existing interface, a new one is built, consequently adding yet more “spaghetti”.
The IT Department headache of data integration between applications
These data interchanges are increasingly business-critical, and IT teams are often forced to make a huge effort to attain the quality of service levels stipulated in SLAs, and that are required by functional management and by customers. Moreover, the widespread use of applications provided in SaaS mode in businesses also makes data integration architecture more complicated for IT Departments, who now are increasingly called upon to manage interchanges with the outside world while simultaneously increasing their information system’s security.
Each time a new application is introduced into the company, the information system architecture becomes a little more complex. The need to make disparate applications communicate with each other while securely managing the data traffic between them can become a real headache.
What is EAI (Enterprise Application Integration)?
It is an approach, software architecture or platform that will ensure communication and inter-application exchanges. It is one of the concepts at the heart of Information System urbanisation.
It generally uses middleware or microservices architecture to act as a layer of intermediation between the various software applications, and to “translate” and route the data so that it can be understood by each component of the Information System.
What is the difference between the concepts of Enterprise Application Integration and Enterprise Service Bus?
EAI focuses on the connection and orchestration of applications within a company to facilitate the sharing of data and information. It is primarily a centralised integration model designed to unify exchanges between heterogeneous systems.
The ESB (Enterprise Service Bus) offers a more flexible and decentralised architecture, acting as a bus or channel that enables applications to communicate via web services modules.
In short, the two concepts are similar: EAI focuses more on application integration (“integration hub”) and ESB on more dynamic and modular inter-application communication (“exchange hub”).

How process (BPM) and data (ESB) integration can create value for IT and business departments ?
EAI tools to improve data integration between applications and keep it secure
In response to these integration issues, Blueway’s Phoenix data platform makes it possible to industrialise the flows exchanged between several applications, within the Information System and also with your partners, using a number of fully integrated tools:
Managing exchange scenarios
An inter-application data interchange scenario management design workshop, using a simple, pragmatic and effective web-only graphical interface.
Testing tools
Unit and integration test kits, enabling full test sets to be run.
Technical connectors
Technical connectors to the main SQL and NoSQL databases, flat files and XML, email, FTP, sFTP, EDI, LDAP, Web services, etc.
Application bus
The native integration of an application bus that provides structured and secure management of interchanges between applications and eliminates the “interface spaghetti” effect.
Impact analysis and refactoring
Impact analysis and refactoring tools to realign data interchange between applications to meet requests from functional departments (changes to or development in component applications, legal or production constraints, and so on).
Application connectors
Standardised application connectors to the main applications on the market (CRM Salesforce, Microsoft Dynamics NAV, AX and CRM, Cegid, Movex, Oracle Applications, Pivotal, SAP, Selligent, Siebel and Sage X3, JDEdwards, Baan, SugarCRM, etc.).
Supervision of exchanges
A fully-integrated data interchange supervision platform delivering a 360° view of how data traffic is running.
The success of interoperability lies precisely in the fact that it is not an issue in the lives of users! To succeed, you need a solution AND the ability to stand back: this means taking a step back from your information system and seeing all the flows that are in circulation.
Edouard Cante, Deputy Managing Director of Products at Blueway

ESB vs ETL ? The distinction between is no longer relevant relative to today’s business requirements.
Here are a few examples of where Enterprise Application Integration platforms can be put to good use:
- Environments historically structured around a central ERP such as SAP. If the company wants to move away from this monolithic vision and support a transformation of its organisation, it will need an inter-application brick.
- Communication between several e-commerce applications (e-commerce site, order management, payment, link with stocks and dispatch). The fluidity of the entire process is a guarantee of competitiveness and customer experience.
- Interoperability within the HR Information System, between different business applications, and also between the HRIS and other IS applications.
- Modernising an information system with a strong legacy component, where it is necessary to decommission applications and facilitate the MCO and scalability of the information system.
- Combining and consolidating the information systems of several organisations, essential in the context of mergers and acquisitions.
Blueway’s Phoenix platform EAI solution to meet the challenges of business agility and interoperability
The many facets of inter-application solutions
Our Phoenix data platform greatly simplifies data handling. You manage data integration between your various applications and those of your partners, customers and suppliers using standardised ETL (Extract Transform Load), ESB (Enterprise Service Bus) and EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) tools.
With more than 160 customers using Blueway’s Phoenix platform, some 1,500,000 data flows are processed, transported and integrated every day.
The users of our platform for integrating their data operate in sectors as varied as industry, healthcare, services, local authorities, pharmaceutical laboratories, the agri-food industry, and so on.
The solution has to combine human and technological roles, position itself at organisational level to provide a response tailored to business needs, and ensure that processes adhere to the information system.

Want to discuss interoperability challenges with an expert?